Questions
Quick questions
You should be able to answer these questions without too much difficulty after studying this TLP. If not, then you should go through it again!
-
Ferrous scrap metal is easily separated from non-ferrous, using an electromagnet. However, non-ferrous metals still need to be separated before recycling. What materials properties allow the separation of non-ferrous metals in the eddy current separator?
-
In the eddy current separator a rotating magnet block causes a changing magnetic flux. The metal is moving through the changing flux and swirling currents are formed as a result. What effect do these swirling currents have?
-
Tin is separated from steel cans using principles involving corrosion. What method is used to decide the conditions of corrosion such that the steel will not dissolve into solution as well?
-
How is the tin removed from the solution?
-
What property of copper could be exploited in order to separate it from steel and other plastics before recycling?
Deeper questions
The following questions require some thought and reaching the answer may require you to think beyond the contents of this TLP.
-
If the calorific value of coal is 30.9 MJ kg-1 and it is combusted at 40% efficiency in a power station, how many kilograms of coal would be needed to produce 1 kg of primary production aluminium and 1 kg of recycled aluminium respectively?
Hence, or otherwise, find a percentage value for the energy saved by recycling aluminium.
-
Today, an increasing amount of metal is being galvanised. In automotives and home appliances the advantage of Galvanised Steel is that even if the Zn layer is scratched, the steel will not rust. This comes from the fact that Zn is much more reactive with O2 than Steel (Fe) and so reacts with the oxygen preferentially. However, in 5 or 6 years when these galvanised items reach the end of their lives, a huge amount of zinc-plated scrap will need to be recycled.
Zn has a boiling point of 907°C. This is a lower temperature than the melting point of steel in the EAF, so if Zn is present in the melt, it boils off and is separated. This forms a vapour. Carbon dioxide gas is also present in these exhaust fumes, and since Zn is highly reactive with oxygen, it displaces the carbon to form ZnO particles. These are in the form of an extremely fine dust that is a problem for workers at EAF plants. It can be collected, although it has to be further refined to become useful Zn (expending more energy).
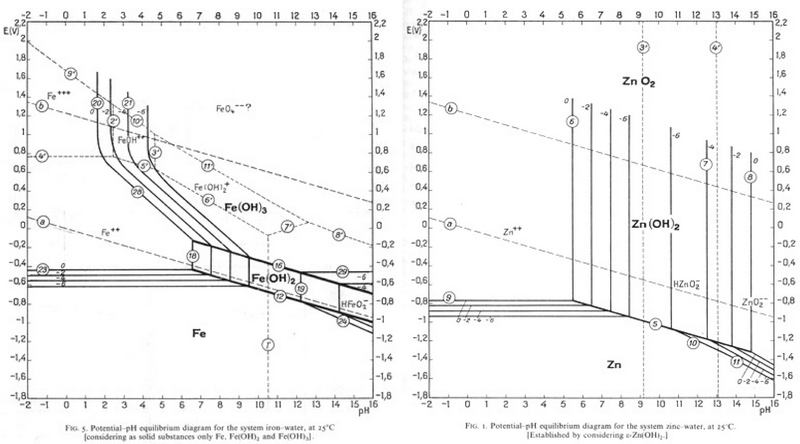
Since Zn is most commonly electroplated to steel, it could be removed in the same way as tin is removed from steel, and this process is currently being researched. Find a pH and an E° value that would allow Zn to be corroded and Fe to be passivated?
-
An exemplar energy calculation for the primary formation of Al is shown in the TLP. Magnesium is another metal that has to be extracted via electrolysis rather than direct reduction with carbon, since it is more ‘reactive’ than carbon.
MgCl2(l) → Mg(l) + Cl2(g)
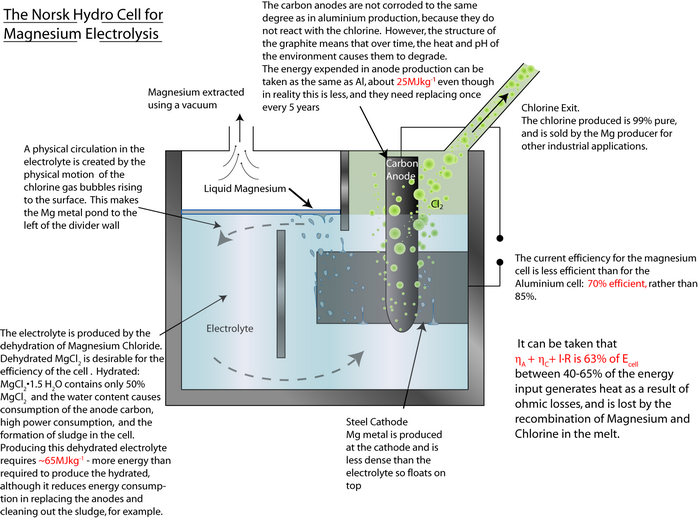
By using the same method as that used in the TLP for aluminium, calculate the energy required to produce 1 kg of magnesium.
-
In the electric arc furnace, conditions are created such that impurities resulting from poorly sorted steel scrap are reduced/oxidised into slag. It was explained in the TLP how the Ellingham diagram can be used to predict which metals will come out of solution with the steel and which ones will not. Phosphorus (P), Copper and Tin cannot come out of solution this way, and other methods have to be employed (as described) to remove them from solution.
It was explained that P is removed from the EAF by addition of CaO to produce a very basic slag.
Why does this occur?
Phosphorus can oxidise to P2O5 as shown:
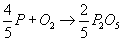
The driving force for P oxidation is lower than that for the oxidation of Fe. Thermodynamically, as depicted in the Ellingham diagram, oxidation of P from Fe melt is not favourable. As the concentration of P in the melt is low, the activity of P in the Fe melt is in the order of magnitude of 10-3, further decreasing the driving force for oxidising and thus removing P from the melt.
It will be possible to remove P from the Fe melt by an oxidation reaction, provided the driving force is greatly increased by achieving a very low activity for P2O5 in the slag in equilibrium with Fe such that P2O5 is transferred from the melt to the slag. For this to happen in the slag, the ΔG value for the oxidation of Fe to FeO needs to equal the ΔG value for P to P2O5.
If we assume that Fe is pure (which is not unreasonable) and the slag is saturated with FeO, ΔG of the reaction:
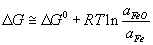
becomes equal to ΔG°, because the activity term
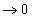 .
.*Note that in practice an oxidising slag actually contains 20 mol% FeO (at which the activity of FeO is ~0.2).
For P to be oxidised into the slag spontaneously, the reaction
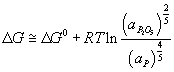
needs to be at least equal the value of ΔG° from the iron reaction.
Since the value of ΔG° for the oxidation of P is known – it can be found from the Ellingham diagram at the temperature within the EAF, one can calculate the required activity of the P2O5 to allow it to move into the slag in the EAF. Find this value.