Re-use of this resource is governed by a Creative Commons
Attribution-
NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
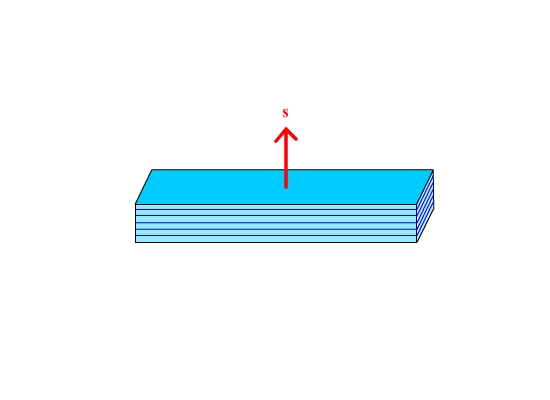
The scattering vector is perpendicular to the planes of interest.
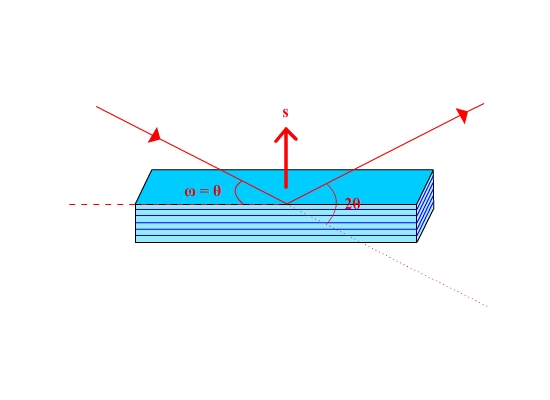
This is the standard symmetric reflection geometry
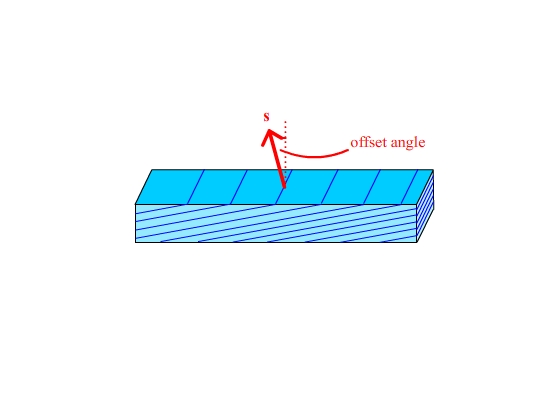
Now the planes, and hence the scattering vector are offset
.

To measure the diffraction peak the sample is rotated by the offset. Now ω is not equal to θ. This is called an asymmetric reflection
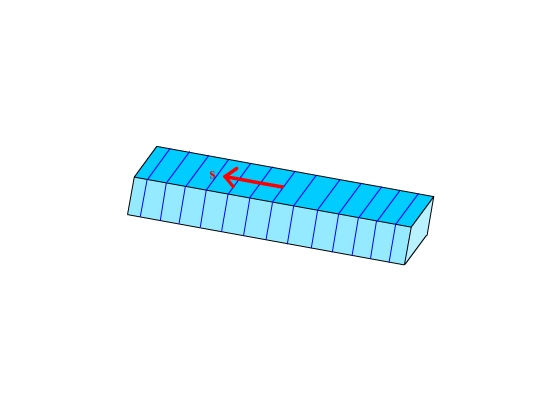
How do we collect reflections from these planes?

This transmission mode is only possible when the X-rays can
penetrate the sample, i.e. a low enough absorption coefficient. Typically
this is possible in polymers.