Micrograph Library
Browse the libraryAdvanced searchSystemsCompositionsTechniquesKeywordsPhase diagramsHelpPreferencesAbout the micrograph libraryTerms of useContribute micrographs!FeedbackLinksCredits Print this page
Micrograph 593 and full record

- Micrograph no
- 593
- Brief description
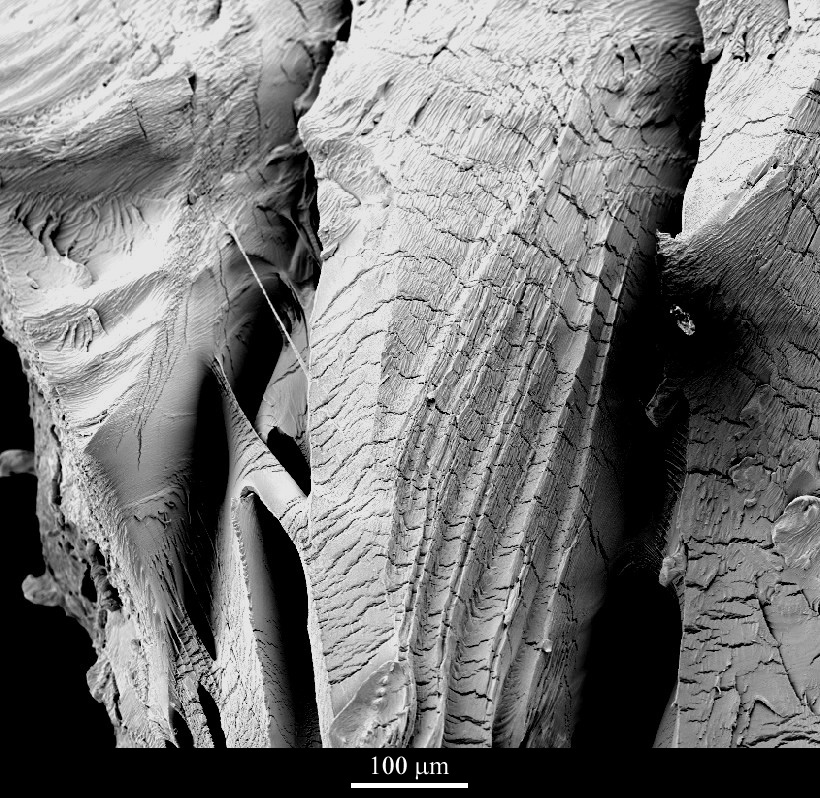
- Ductile tearing near a fracture surface in polycarbonate
- Keywords
- craze
 , ductile
, ductile  , ductile tearing, fibril
, ductile tearing, fibril  , fracture
, fracture  , polycarbonate (PC), polymer
, polycarbonate (PC), polymer 
- Categories
- Fracture, Polymer
- System
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Composition
- Not specified
- Standard codes
- Reaction
- Processing
- Applications
- Polycarbonate is a clear and relatively tough plastic used to make shatterproof windows, lenses and even helmets. It is also used to make compact discs.
- Sample preparation
- To induce crazing and fracture in polycarbonate, acetone is used. This results in the otherwise tough material becoming very brittle
- Technique
- Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
- Length bar
- 100 μm
- Further information
- The fracture surface is dominated by ductile tearing, and also shows linear voids with fine transverse filaments. These are the remnants of crazes which act both as a precursor to cracking and as a toughening mechanism. In some areas, more angular brittle fracture surfaces are also apparent. The fine-scale ridging of the surface, parallel to the principal stress direction (which is approximately vertical) morphology is the result of fibrous crystals being induced by cold-drawing.
- Contributor
- J A Curran
- Organisation
- Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy, University of Cambridge
- Date
- 03/10/02
- Licence for re-use
 Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International- Related micrographs
View image alone .. in a new window
Help is available on downloading images