Re-use of this resource is governed by a Creative Commons
Attribution-
NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
Applications: Maglev Trains

There are two basic designs of magnetically levitated
(maglev) train. Click on the buttons above to investigate the workings
of the two desgins.
Levitation Systems
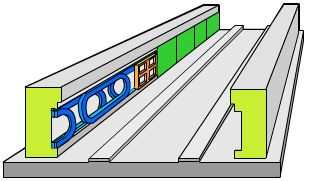
In electrodynamic suspension (EDS) systems, superconducting
magnets are used to create repulsive forces which lift the train off
the rails. This means that the field does not have to be adjusted due
to the more stable nature of the repulsion. However, it does mean that
there are significant fields within the train carriages and that the
train has to be wheeled at low speeds.
Roll over the track to investigate the system in more detail.
Beams
Wheel tracks
Support
Propulsion coils
Levitation and guidance coils
Suspension Systems
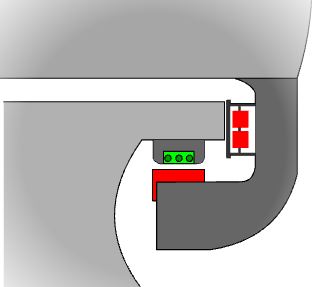

In electromagnetic suspension (EMS) systems, superconducting
magnets are used to create an attractive force which lifts the train
up. This requires constant measurement and alteration of the field strength
to keep the separation between the magnets constant. However, this system
has negligable fields within the train and requires no secondary propulsion
system.
Roll over the track to investigate the system in more
detail.
Guide Magnets
Current in Track
Train Magnet