Questions
Quick questions
You should be able to answer these questions without too much difficulty after studying this TLP. If not, then you should go through it again!
-
What is the main difference between hardwoods and softwoods?
-
How do wood's materials properties change when wet?
-
What deformation characteristic does wood show on three-point bend testing?
-
By what mechanism does wood fail on loading during three-point bend testing?
-
Which of the following is not present in a plant cell?
-
Which region of the yew tree is used to make longbows?
Deeper questions
The following questions require some thought and reaching the answer may require you to think beyond the contents of this TLP.
-
Below is shown a 3D model of the trunk interior of balsa made from slides taken in the tangential, radial and transverse directions. Identify the key features on this 3D balsa wood sample:
-
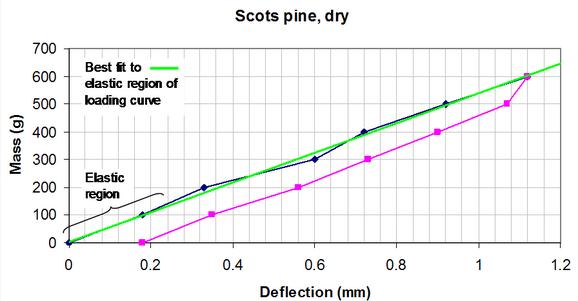
Calculate the percentage of elastic strain energy that is stored in a loading-unloading cycle for a wood sample.
-
Calculate the stiffness of this wood sample given the previous graph of loading and unloading for Scots pine.
-
(…continued from previous question) Now calculate the strength of the wood sample using the following results:
L (cm)
9.0 ± 0.1
w (mm)
3.20
h (mm)
3.30
mass (kg)
1.7 ± 0.05
Use g = 9.81 m s-2
-
(...continued from previous question) What are the errors in your calculated values of stiffness and strength?
-
What wood, out of the following, would be used to make a cricket bat blade?
a Willow: Tough, light and resilient
b Cane: Light and springy.
c Birch: Inexpensive, tough and heavy.
d Elm: Very easy to bend, good durability and easy to work.