Micrograph Library
Browse the libraryAdvanced searchSystemsCompositionsTechniquesKeywordsPhase diagramsHelpPreferencesAbout the micrograph libraryTerms of useContribute micrographs!FeedbackLinksCredits Print this page
Full Record for Micrograph 176
[538 KB]
View micrograph
.. in new window
View micrograph and record
.. in new window
You can also view and download the micrographs on Flickr
- Micrograph no
- 176
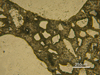
- Brief description
- Concrete from a commercial paving slab
- Keywords
- aggregate, cement
 , ceramic
, ceramic  , concrete
, concrete  , water
, water - Categories
- Ceramic, Composite
- System
- Concrete
- Composition
- Aggregate, cement, water
- Standard codes
- Reaction
- Processing
- Made from aggregates (sand, crushed rock or gravel), bound by cement and water. Cement consists of crystalline minerals of calcium aluminates and silicates, held together by a silicate gel produced during a hydration reaction.
- Applications
- Many uses in the construction industry, such as buildings and bridges and paving slabs.
- Sample preparation
- Polished but unetched
- Technique
- Reflected light microscopy
- Length bar
- 250 μm
- Further information
- Concrete is 8 times stronger in compression than tension, so is usually designed for compressive rather than tensile loading. Tensile strength can be increased by pre-stressing the concrete using steel wires that are held in tension during setting. When the stress on the wires is removed, they contract forcing the concrete into compression. When the concrete is then subjected to a tensile stress, the internal compressive stress has to be exceeded before the concrete goes into tension
- Contributor
- Dr K M Knowles
- Organisation
- Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy, University of Cambridge
- Date
- 09/08/02
- Licence for re-use
 Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International- Related micrographs