Questions
Quick questions
You should be able to answer these questions without too much difficulty after studying this TLP. If not, then you should go through it again!
-
Which are the conditions that define ideal elastic behaviour? (You may pick more than one answer)
-
Which of the mechanical behaviours below is time dependent? (You may pick more than one answer)
-
The animation below shows the linear elastic behaviour of copper, calculate its Young’s Modulus E.
(a) 130 GPa
(b) 130 MPa
(c) 130 kPa
(d) 130 Pa -
Select the mechanical process responsible for plastic deformation. (You may pick more than one answer)
-
Dislocation glide is temperature dependent. As the temperature drops, a metal may transform from ductile to brittle (i.e. it undergoes less plastic deformation). The crystal structure affects the ductile brittle transition temperature because (you may pick more than one answer)
-
Calculate the stresses inside a pressurised thin-wall (i) spherical and (ii)cylindrical vessels from the diagrams below.
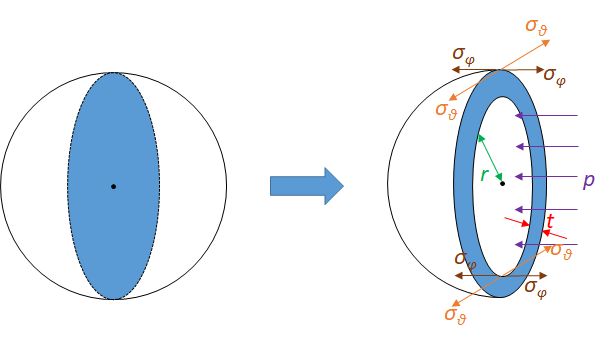
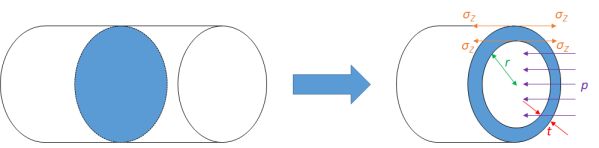
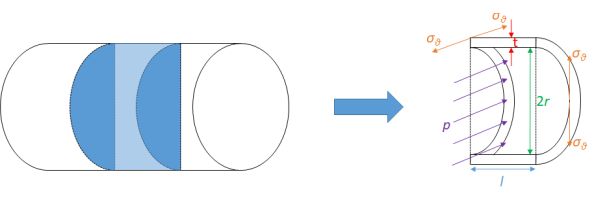
-
The elastic properties of natural rubber (cis-1,4-polyisoprene) can be represented by the Maxwell model of a spring (with stiffness k) and a dashpot (with viscosity ν) in series. When subjected to an oscillating stress at angular frequency, ω, the effective Young’s modulus E of the rubber is given by
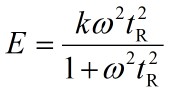
where the characteristic relaxation time, tR, is given by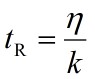
(i)Obtain an expression for E at high and low ω.
(ii) Sketch the variation of E as a function of ω2.
(iii) If the temperature is higher, how will the sketch change? -
Consider a rolling mill below to reduce the cross section area of the workpiece.
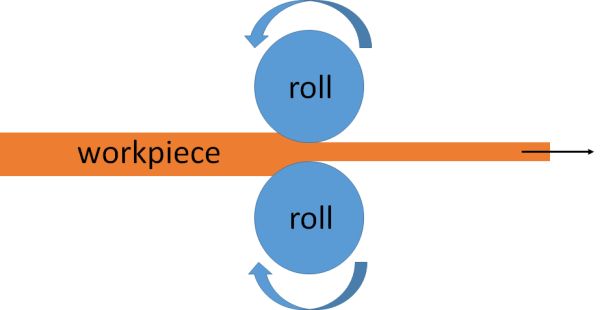
The increment of plastic work done on drawing a cylinder of cross sectional area A and length L an amount δL is given by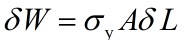 where σy is the uniaxial yield stress of the component material. Here we assumed no work hardening, so the applied force is σyA.
where σy is the uniaxial yield stress of the component material. Here we assumed no work hardening, so the applied force is σyA.
From this expression, find an expression for minimum amount of work per unit volume, Up required to deform plastically a component with reduction ratio R (> 1).