Micrograph Library
Browse the libraryAdvanced searchSystemsCompositionsTechniquesKeywordsPhase diagramsHelpPreferencesAbout the micrograph libraryTerms of useContribute micrographs!FeedbackLinksCredits Print this page
Full Record for Micrograph 187
[113 KB]
View micrograph
.. in new window
View micrograph and record
.. in new window
You can also view and download the micrographs on Flickr
- Micrograph no
- 187
- Brief description
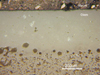
- Part of a Denby pottery mug, showing the glaze on the surface
- Keywords
- ceramic
 , clay, glaze, pottery, vitrification
, clay, glaze, pottery, vitrification - Categories
- Ceramic
- System
- Al2O3-SiO2
- Composition
- Mostly clay (which consists of alumina and silica)
- Standard codes
- Reaction
- Processing
- Firing, which causes vitrification of the clay
- Applications
- Crockery
- Sample preparation
- Polished but unetched
- Technique
- Reflected light microscopy
- Length bar
- 200 μm
- Further information
- On firing, water trapped within the clay evaporates as the temperature rises. Vitrification occurs above about 1000ºC, and the clay material fuses into a dense glassy material. Aluminium silicate crystals bond the matrix, increasing the strength, and the object shrinks and becomes more dense. Glaze is then applied, which vitrifies when the object is fired again, and bonds to the surface making it waterproof.
- Contributor
- Dr K M Knowles
- Organisation
- Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy, University of Cambridge
- Date
- 09/08/02
- Licence for re-use
 Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International- Related micrographs