Micrograph Library
Browse the libraryAdvanced searchSystemsCompositionsTechniquesKeywordsPhase diagramsHelpPreferencesAbout the micrograph libraryTerms of useContribute micrographs!FeedbackLinksCredits Print this page
Full Record for Micrograph 611
[139 KB]
View micrograph
.. in new window
View micrograph and record
.. in new window
You can also view and download the micrographs on Flickr
- Micrograph no
- 611
- Brief description
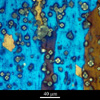
- Section of a metal matrix composite (MMC) after extrusion and annealing
- Keywords
- alumina
 , annealing
, annealing  , coincidence site lattice (CSL), composite material
, coincidence site lattice (CSL), composite material  , extrusion
, extrusion  , island grains, MMC, nucleation
, island grains, MMC, nucleation  , particle, stringers
, particle, stringers - Categories
- Composite
- System
- Al
- Composition
- Commercial purity (99.5%) + 13 micron alumina spheroids
- Standard codes
- Reaction
- N/A
- Processing
- Commercial purity (99.5%) aluminium has been atomised, thoroughly mixed with alumina reinforcement particles and then extruded.
- Applications
- Metal matrix composites (MMCs) offer high specific stiffness which can be retained to high temperatures. This makes them suitable for applications in the aerospace industry. They also offer controlled (or zero) thermal expansion coefficients, good wear resistance and good impact properties.
- Sample preparation
- The sample has been oxidised to provide colour contrast for different grain orientations.
- Technique
- Reflected light microscopy, polarised
- Length bar
- 40 μm
- Further information
- Commercial purity aluminium has atomised, mixed with 13 micron spherical alumina particles, ball milled, tumbled, cold compacted (20MPa) and then extruded (with the working direction vertical in the image). It has then been annealed at 630 degrees C. Vertical stringers of fine oxide particles are visible. Note the small yellow 'island' grain which has formed within one of the recrystallised grains and is likely to have nucleated on the adjacent reinforcement particle. Note also the boundary facets of some grains. These indicate a preferred habit plane and are probably coincidence site lattice (CSL) boundaries.
- Contributor
- Prof T W Clyne
- Organisation
- Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy, University of Cambridge
- Date
- 03/10/02
- Licence for re-use
 Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International- Related micrographs