Micrograph Library
Browse the libraryAdvanced searchSystemsCompositionsTechniquesKeywordsPhase diagramsHelpPreferencesAbout the micrograph libraryTerms of useContribute micrographs!FeedbackLinksCredits Print this page
Full Record for Micrograph 638
[143 KB]
View micrograph
.. in new window
View micrograph and record
.. in new window
You can also view and download the micrographs on Flickr
- Micrograph no
- 638
- Brief description
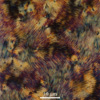
- Disclinations in a smectic LCP, revealed by decoration
- Keywords
- alignment, decoration, disclination, dislocation
 , liquid crystalline polymer (LCP), polymer
, liquid crystalline polymer (LCP), polymer  , smectic, spontaneous band texture, texture
, smectic, spontaneous band texture, texture - Categories
- Polymer
- System
- Liquid crystalline polymer
- Composition
- Semi-flexible LCP, Cl-8
- Standard codes
- Reaction
- Processing
- The band texture forms spontaneously during the solidification of smectic melts of some semi-flexible polymers. It may also be induced by shear.
- Applications
- The molecules in a LCP mesophase can be steered by external fields; a property used in display technology. Alignment is also exploited in high strength fibres like Kevlar and mouldable Vectra.
- Sample preparation
- Technique
- Cross-polarised light microscopy
- Length bar
- 10 μm
- Further information
- Detailed configurations of disclinations and their interactions have been elucidated by band texture decoration. The positive value of elastic anisotropy of a semi-flexible LCP, Cl-6, shows that bend distortion is favoured. The obvious variations of elastic anisotropy values measured from the different disclinations is probably related to the polydispersity of the polymer. The majority of disclination pairs showing random configurations indicate that that defect interactions are far from equilibrium in polymeric smectics.
- Contributor
- Prof A H Windle
- Organisation
- Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy, University of Cambridge
- Date
- 03/10/02
- Licence for re-use
 Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International- Related micrographs